
Anticoagulants, antiplatelet therapy (e.g., aspirin, ADP receptor inhibitors).Invasive management depends on risk stratification (e.g., TIMI score).

ST elevations (in two contiguous leads) or new left bundle branch block with strong clinical suspicion of myocardial ischemia.Normal or nonspecific (e.g., ST depression, loss of R wave, T-wave inversion).
#Timi score for stemi full
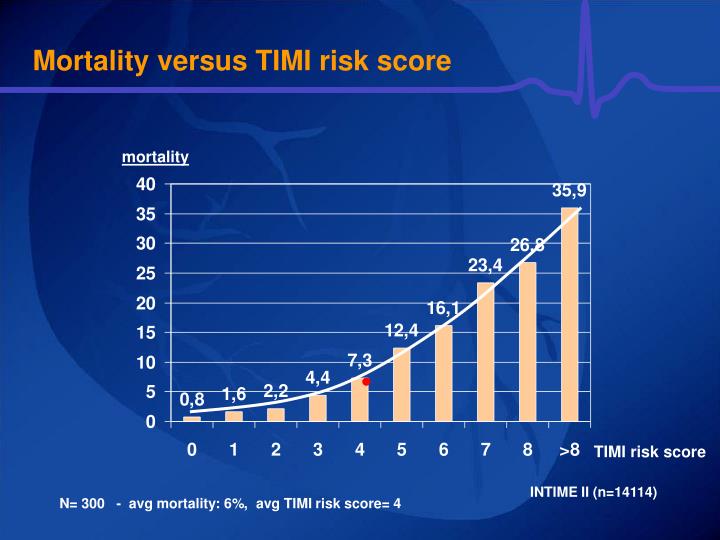
Affects the full thickness of the myocardium ( transmural infarction). Classically due to complete occlusion of a coronary artery. Affects the inner layer of the heart ( subendocardial infarction). Classically due to partial occlusion of a coronary artery. Partial occlusion of coronary vessel → decreased blood supply → ischemic symptoms without infarction. Autonomic symptoms may be present: diaphoresis, syncope, palpitations, nausea, and/or vomiting. Severe, persistent, and/or worsening ( crescendo angina). Occurring at rest/with minimal exertion and is usually not relieved by rest or nitroglycerin. Symptoms are not reproducible/predictable. Acute myocardial ischemia that is severe enough to cause ST-segment elevations on ECG. Acute myocardial ischemia that is severe enough to cause detectable quantities of myocardial injury biomarkers but without ST-segment elevations on ECG. Acute myocardial ischemia that is not severe enough to cause detectable quantities of myocardial injury biomarkers or ST-segment elevations on ECG. ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction ( STEMI) Non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction ( NSTEMI) Overview of acute coronary syndrome ( ACS) See “ Myocardial infarction” for more details regarding, e.g., histopathology and long-term management. This article concerns the initial management of ACS patients. Adjunctive therapy (e.g., beta blockers, oxygen) helps reduce symptoms and can have a positive impact on mortality. All ACS patients receive dual antiplatelet therapy and initially anticoagulation. The timing and necessity of revascularization therapy in NSTE-ACS is determined based on multiple risk factors. STE-ACS patients require immediate revascularization therapy with percutaneous coronary intervention ( PCI) or fibrinolytic therapy. Depending on serum levels of cardiac troponin (cTn), NSTE-ACS can be categorized as NSTEMI or unstable angina (UA). Based on ECG findings, patients are categorized into those with ST-elevation ( STE-ACS) or non- ST-elevation ACS ( NSTE-ACS). Clinical findings (e.g., onset and characteristics of pain, patient history) in combination with ECG and troponin are the mainstays of diagnosis. Killips categorization grade 2-4 had the highest relative risk (RR-15.85) of the seven potentially dubious variables evaluated, followed by systolic BP 100mmHg (RR-10.48), diabetes mellitus (RR-2.79), and age >65 years (RR- 2.59).Ĭonclusions: In patients with STEMI, the TIMI risk scoring system appears to be a straightforward, valid, and practical bedside tool for quantitative risk classification and short-term prognosis prediction.Acute coronary syndrome ( ACS) is the clinical manifestation of myocardial infarct and commonly the default working diagnosis in patients with new-onset chest pain suspected to be of cardiac ischemic origin. The highest mortality rate (total 17 deaths) was found in the high-risk group (55.6%), followed by moderate-risk (12.2%) and low-risk (1.28%) groups, respectively. Results: According to the TIMI risk score, 79 patients (54.5%) had low-risk, 48 (33.1%) to the moderate-risk, and 18 (12.4%) to the high-risk. All patients received standard anti-ischemic medication, were thrombolyzed, monitored in the ICCU, and monitored throughout their hospital stay for post-MI sequelae. Based on their TIMI scores, the patients were placed into three risk groups: low-risk,moderate-risk, and high-risk. Methods: 145 STEMI patients were included in this srudy, TIMI risk scores were calculated and analysed vis-Ã -vis various relevant parameters. An attempt was made to assess the situation by comparing risk stratification based on the TIMI score with the hospital outcome of such individuals. Background: The Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) risk score is said to be an important factor in predicting mortality risk in fibrinolysis-eligible STEMI patients.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
